
The e-bike industry is up and growing with the increasing number of consumers who prefer to secure a ride of their own. E-bikes have become very popular as many commuters have preferred sustainable transportation means.
An electric bicycle, or e-bike, is a bicycle that has an electric motor, optionally used for propulsion, that can operate in pedal-driven, pedal-assisted, or power-on-demand mode. It is designed with a battery, motor, and controller, which are all combined into one system.
In this ultimate guide and explainer, we will guide you point-by-point on all topics that discuss the most fundamental to the most complicated details about electric bicycles.
Electric Bicycles: The Origin
Known as an e-bike with varied functionalities it is not an electric motorcycle because it can be pedaled by its rider. Legally classified as bicycles, electric bikes through time have been exempted from stricter laws, particularly on registrations or certifications. These lapses in government regulations throughout history have allowed further evolution of the electric bike. Various companies have exerted efforts to improve the mechanisms of this motorized bicycle.
It all started in the 1890s, when several U.S. patents for electric bicycles were submitted, such as the battery-powered bicycle of Ogden Bolton Jr. and Hosea W. Libbey of Boston, who invented the e-bike driven by a “double electric motor.” In less than a decade, an e-bike using a driving belt was patented by Matthew J. Steffens. This was further improved by John Schnepf using a rear-wheel friction “roller-wheel.”.
The late 1990s revealed the development of torque sensors and power controls such as that made by Takada Yutky of Japan in 1997. Around 1992, no commercial e-bike was made available aside from the ‘Zike’ using NiCd batteries. It was in 1993 that the Japanese automotive giant developed prototypes of an e-bike with a pedal-assist system.
In the same year, Lee Iacocca founded EV Global Motors and in 1997 produced an electric bicycle model named E-bike SX that became the earliest effort to popularize e-bikes in the United States. Since 1998, e-bike usage around the globe has reached impressive growth with China as the biggest manufacturer.
In 2001 the electric bicycle became known as a power bike, e-bike, “pedelec,” pedal-assisted, or power-assisted bicycle. In 2004 alone, an estimated 7.5 million e-bikes were sold in China replacing small motorcycles. In 2016, around 2 million were sold in Europe, specifically in Germany where it’s gaining much popularity.
The Main Components of Electric Bicycles
Similar to regular bikes, an electric bike has the basic parts as we know it. What differentiates a regular bike from an e-bike is the electric component meant to provide support to the rider. Motor power provides greater torque to overcome obstacles like rough roads to guarantee travel and transport without much effort.
Greater attention should then be given to the mechanism and performance of an e-bike according to its components. The e-bike range is key in gauging a smooth ride which implies motor efficiency, battery capacity, and efficiency of the electronic controller. These factors should all be working together for an easier ride.
Motor
The electric bike motor is a factor that has to be considered in the overall e-bike mechanism. The design and location of the motor control torque or power of the e-bike, which is placed in different areas with corresponding effects on the e-bike’s performance. The motor is either integrated into the front hub or at the center of the e-bike’s frame, i.e., the mid-drive.
Cheaper hub drives are found on the rear or front wheel of an e-bike. When engaged, the hub drive pulls or pushes on the wheels. However, since the hub drive is not connected to the bike’s gears, its power is less efficient in rugged or uphill terrain. This kind of motor is found to accelerate better on flat roads. Surely it can bring you places for a longer period, but never with optimum speed.
Another e-bike motor is the mid-drive, which is considered more expensive compared to the hub drives. This type of electric motor assist is placed between an e-bike’s crank center near the bottom bracket. This motor is currently increasing in popularity as its motor produces greater torque that supplements pedaling power within the bike’s drive.
This motor maximizes the e-bike’s performance to a smooth rider cadence of 50 to 80 RPM. This allows mid-drive motors a straight, low-speed climb on higher or rugged terrain. The mid-drive motor gives a better balance because of its position in the center of the e-bike frame.
Battery
These are crucial to e-bike range and operation. Although the energy cost of e-bikes is low because they do not need fuel or gas, battery replacement is still costly.
The rechargeable battery on an electric bicycle is placed depending on its frame and size. The average charging time is around five to six hours and is entirely dependent on the battery type and model.
E-bike batteries are either sealed lead acid (SLA), which is more affordable but heavy and bulky. They require more maintenance and have a shorter life span, which lasts for only 100-300 full cycle charges.
However, nowadays most riders prefer lightweight batteries that are (**are) low-maintenance, such as the lithium battery, which is maintenance-free and can be charged around 800 times. This is 2-3 times higher than the SLA battery. Better features mean a higher price for you, but it’s worth the battery price and overall battery life.
Controller
Made with varied designs, the controller is found on the handlebar. This part of your e-bike allows you to operate electric assistance with great ease.
Pressing down on the e-bike’s pedal will activate the controller if it is equipped with pedal-activated systems. In this system, the controller allows adjustment of the assistance level according to how you apply pressure to the pedal.
If your e-bike is throttle-based, then the controller will work by pulling back or pressing the throttle. The most common designs are either with a twist-grip type or a thumb-press type. In this type of e-bike, there is no need to pedal for the activation of the electronic assistance mechanism.
Electric Bike Classifications
E-bike classification is based on their torque or power, which comes from their electric motor. The treatment of e-bikes varies across countries and jurisdictions, which affects how they are categorized. Such is the case of federal laws in the US, where the nature of e-bikes is still being defined. It is a question of whether e-bikes should be considered regular bikes or motorcycles.
The impressive increase in the demand for e-bikes resulted in the move to update rules and regulations relevant to the presence of more e-bike riders on the streets, especially in the US. To date, there are eleven states which have defined e-bikes within the three classes.
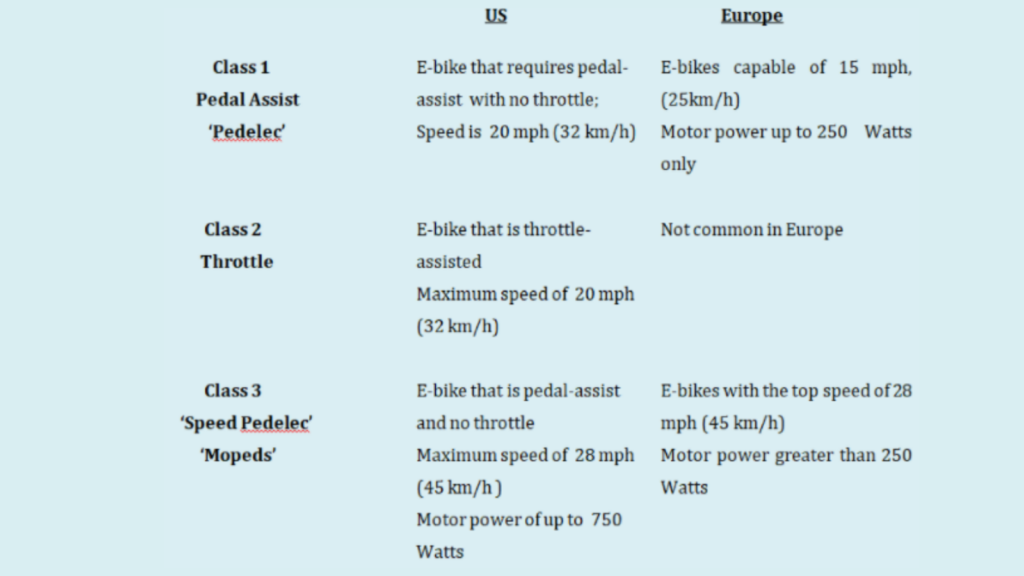
Class 1: The ‘Pedelec’ or ‘Pedal-Electric Bikes’
This is so far the most common type of electric bike. This type of e-bike is known as ‘pedelec’ or pedal assist. The motor of this e-bike only assists while the rider pedals to increase the power or torque being transmitted to the e-bike wheel. This helps you to ride longer distances or to speed uphill.
In Europe, this system is considered Class 1 with motor power only up to 250 watts. The allowed maximum speed in Europe is 15 mph (25 km/h). In the case of the Class 1 e-bike in the US, its speed is limited to 20 mph (32 km/h). This is why this class of e-bikes is allowed on the road where regular bikes can pass and with no license required from the rider.
Class 2: Throttle
A throttle or Class 2 e-bike propels without the use of the pedal up to a top speed of 20 mph (32 km/h) in the US and up to 15 mph (25 km/h) in Europe. Similar to a scooter or a motorcycle, it can provide enough power according to how much we press on the throttle.
Class 2 e-bikes are largely prohibited by laws in many countries, unlike pedal-assist e-bikes. In the case of the European Union, it is required that pedals allow the e-bike to move forward while power is being provided by the motor. However, in the case of the United States, this class is very common, as no law prohibits its use.
Class 3: Speed Pedelec or ‘Mopeds’
The Speed Pedelec, or ‘Schnell-Pedelecs’, are legally classified as ’ mopeds’ with an engine that has a capacity of fewer than 50 ccs. Classified as Class 3, this electric bicycle has a design that is similar to the common ‘pedelec’ but its speed can reach up to 28 mph (45 km/h). Such speed demands a corresponding motor vehicle license, as its motor power can be greater than 250 watts. This e-bike is popular among commuters because they are faster and will surely keep you up with the traffic.
Modes of Operation
Electric bicycles are here to make transport easier. It was manufactured with a design that will make it easy to operate. Every rider should be aware and skilled in these available e-bike modes:
The Pedal Mode
Use of the e-bike pedal is as smooth as your regular bike and without any resistance. The motor of the e-bike will never be an issue here as you push on the pedals of the e-bike to allow its acceleration.
Pedal-Assist or Electric-Assist Mode
This mode combines the use of the pedal and the motor’s electric power. When you set this mode, the motor will slowly provide you with the push as you start to pedal on the e-bike. You will notice that there is greater power or torque as you push on the pedal. Some models allow you to change gears and choose the motor power by switching from low or 30%, medium or 60%, and high or 100% or power to assist you in pedaling.
Electric-Only Mode
In this mode, you can sit back and relax. The motor will propel the bike and allow you to just go along. You can pedal afterward or come to a full stop. However, take note that the top speed for this mode is limited to 28 mph in the US and 45 km/h in Europe, as regulated by federal laws.
Quality Warranty
The demands for e-bikes across the globe have remarkably surged in the last few years. This, in economic terms, means that manufacturers have scrambled (especially in China) to mass-produce all classes of electrical bikes. Prices of e-bikes have decreased as a result of this large-scale production. Electric bikes have become more affordable nowadays. Many can afford to get a hold of even the most basic Class 1 e-bike or the so-called ‘pedelecs’.
Indeed, the market offers cheaper electric bikes, but many of them have serious and frustrating caveats. Some manufacturers give false promises, but they do not deliver. Hence if you are searching for your first e-bike, then anticipate the returns rather than the amount you need to pay for a more expensive e-bike. Eventually, it will be more beneficial to purchase the pricier e-bike model that will guarantee safety and optimal performance.
The Key Accessories
E-bikes are now equipped with a range of accessories to give you a smooth ride. These systems were integrated within the e-bike functions, and they include the following:
Lighting: This is a must-have E-bike safety feature, usually with varying designs and colors. Lighting varies according to e-bike quality, with high-end units having the best lighting systems. Every rider needs this to ensure safe travel, especially during nighttime when road visibility is poor.
LCDs: This electronic display helps to determine and monitor your e-bike’s battery life, mileage, and speed. This LCD is placed on the e-bike’s handlebar and permits easy viewing of the e-bike’s actual speed as well as the status of its battery life.
Smartphone integration: This feature is usually found in high-end e-bikes with top-of-the-line electronics. This feature can be connected through Bluetooth with your smartphone or handheld gadgets. Mobile applications (Apps) such as GPS help you to determine your current geo-location. Through these installed apps, you can surely have a fun-filled and more enjoyable ride.
Built-in security: High-end electric bikes come with a built-in security feature that is made with a matching bike lock. This can be keyed on the rear-wheel locks, which are attached to the frame, while some locks are placed on the e-bike battery. This provides peace of mind to riders, especially when they need to leave their e-bike in public places where parking is not secured.
Rack: These racks are features integrated especially in e-bikes to carry loads. Usually sturdy and durable, you should make sure that these racks perfectly fit your e-bike. These racks can be installed on common e-bikes or high-end electric bikes to allow the carrying of your extra load.
Regulatory Laws on E-Bike Use
The use of electric bikes still creates confusion among riders in varied cities all over the globe, as the use of e-bikes is fairly new. Hence, the law still considers electric bicycles as similar to regular bicycles if the two elements set by federal limits are met. These elements include the e-bike’s top speed, which could only be 20 mph, and its motor power, which could not exceed 750 W.
Since most e-bikes are not subjected to insurance, licenses, and even registrations, it should instead be understood that personal safety must be the paramount concern of regulatory laws. Hence, you should use a quality helmet, efficient lights, and reflectorized gear, whether or not the federal law has cited the same. The current laws state that for Class 3 e-bikes, helmets must be used by riders sixteen years old and older only.
Many countries now require e-bike manufacturers to include a label on their e-bikes before they are released on the market. Such a label must show the e-bike’s type with its corresponding wattage. This in effect will aid law enforcers in carrying out rules relevant to the e-bikes’ speed limits, pathways, and rider’s use of equipment.
Maintaining the E-Bike
Electric bicycles help you to get around. It is a wonderful way to transport you just about anywhere in your community with a very minimal cost and maintenance. Neglecting your e-bike means a bigger problem down the road. Regular maintenance of your electric bike will keep it in top shape.
Maintenance requires a look into the mechanical and electrical components of your e-bike. Your e-bike has mechanical parts that are similar to a regular bike plus the electric motor which deserves the following regular routines.
Regular Cleaning
This will keep dust, mud, dirt, and all other debris from affecting the electric motor and moving parts. A clean motor means a smooth ride since there is no grinding or blocking within the motor mechanism. Using the right shampoo, clean rags, and water once or twice a week is enough to make sure that your e-bike is fresh and clean. Just make sure that the electrical systems in your e-bike are secured and dry. Do not use pressurized water too close to the motor, hubs, and those greased parts of the e-bike.
Use Lubricants or Oil
Applying a decent lubricant is important to keep your e-bike mechanism in perfect condition. Lubricants should be applied to the moving e-bike parts such as the chain at least once a week. You should buy the right lubricant from a reliable e-bike shop because these solutions are chemicals that may adversely affect your e-bike’s spare parts.
Check on Loose Areas
Once a month, it would be necessary to check on possible loose nuts, bolts, and screws on your e-bike. This is life-threatening as it may cause a possible road accident if unchecked. This procedure should be immediate and regular, but not exaggerated. Over-tightening these small e-bike parts can result in a loose thread that is unsafe during travel.
Check Tires
Maintenance means regularly checking on your e-bike’s tires. It should have the right amount of pressure—not too much and not below the ideal. Nobody would want to ‘run flat’. So, you must always use a pressure gauge. Check your tires regularly and inflate them according to the indicated pressure written on the tire.
Check on Your Brake Pads
It is essential to check on your brake pads at least once a month. A failing brake can cause a tragic accident. This is especially necessary during a wet season when the road is usually wet. Failing brake pads should be replaced all at once. This e-bike component is crucial to any rider’s safety on the road.
Check on Your Batteries
Electric bikes primarily get the power from their motor, which is largely dependent on the e-bike’s battery. This is the main electrical piece found within the e-bike. Proper charging of the battery allows it to have a longer life. Improper charging will damage it and possibly discharge it permanently. Keeping your battery topped up will prevent battery replacement and unwanted costs.
The Takeaway
It is said that electric bikes are the sustainable future of transportation. With its rising popularity amid the need for social distancing, the rising gasoline prices, issues on climate change, and traffic jams pervading every city across the globe, there’s no question that electric bikes provide the most potent solution. Acquiring and using energy-efficient electric bikes is the next big step in the right direction to achieving a healthier and cleaner planet.
Did you find this guide helpful? Comment now!



One Response
Glad to be one of the visitors on this awesome website : D.